Deep Dives
Tretinoin vs. Isotretinoin (Accutane): What's the Difference?


SHARE
Deep Dives
Tretinoin vs. Isotretinoin (Accutane): What's the Difference?
Medically reviewed by Aimee Paik, MD
Written by Apostrophe Team
Last updated 4/5/2024
When it comes to acne medication, there's no debate like tretinoin vs. isotretinoin. They are two of the most effective, widely used medications on the market for treating acne. But time and time again, people ask us which one is better.
Despite their similar names and purpose, tretinoin and isotretinoin are very different drugs. One is a topical cream, gel or solution with relatively mild side effects that’s used to specifically target facial acne and reduce certain signs of aging.
The other is an oral medication that’s primarily used to treat severe cases of acne and has a far greater range of potential side effects.
In this guide, we’ll look at the key differences between tretinoin vs. isotretinoin. We’ll also cover the specific advantages and disadvantages of each medication to help you understand which is the best option for your needs.
What Is Tretinoin?
Tretinoin is a topical medication that’s used as both an acne and anti-aging treatment. Tretinoin comes in a range of forms, the most popular of which are topical creams and gels. It’s sold under a variety of brand names, including Retin-A® and Renova®.
Like other retinoids, tretinoin is a derivative of vitamin A. The medication increases the speed at which skin cells die and regrow, resulting in increased cellular turnover. This helps to prevent the development of acne and reduces the impact of aging on your skin’s appearance and quality.
Tretinoin can take several weeks and even months to take effect, during which many users experience a “purge” of acne symptoms. The side effects of tretinoin are relatively mild and are usually limited to an increase in skin dryness, mild skin irritation and skin peeling due to faster cell turnover.
In the United States, tretinoin is only available on prescription. In cream and gel form, it comes in a variety of concentrations, ranging from relatively mild 0.01 percent tretinoin creams to stronger 0.1 percent solutions.
What Is Isotretinoin?
Isotretinoin is an oral medication that’s designed to treat and prevent acne. Commonly sold as Accutane, isotretinoin is usually prescribed by dermatologists to treat recurring cases of acne that don’t respond to other treatment options.
Isotretinoin is viewed by many healthcare providers as the most powerful and effective treatment available for acne. But, as we know, with great power comes great responsibility. Many dermatologists use isotretinoin to treat only the most severe acne, including cystic acne, over the course of several months of treatment.
Like tretinoin, isotretinoin can take several weeks to produce results, during which many people experience a temporary increase in acne symptoms.
Isotretinoin side effects are also notably far more severe than those of tretinoin. Because there's currently no topical isotretinoin and it only comes as an oral medication, it affects skin across the entire body and can cause everything from dryness to itching, cracked lips, rashes, joint pain and changes in the growth of fingernails and/or toenails.
Oral isotretinoin can also be harsh on the body’s lipids and liver enzymes. For this reason, most healthcare professionals recommend regular blood tests to patients using isotretinoin to minimize the risk of severe side effects from the medication.
In simple terms, isotretinoin is a more powerful option for treating acne than tretinoin, both in its positive effects and in its potential side effects. As such, it’s normally used as a last resort option for patients with severe acne that hasn’t healed using other treatments. However, because there's currently no type of topical isotretinoin, it's important to remember using it will affect your entire body, as opposed to the spot treatments offered by tretinoin.
Tretinoin vs. Isotretinoin: Side Effects
Because tretinoin is a topical medication and isotretinoin is an oral medication, the two different drugs have significantly different side effect profiles.
The most common side effects of tretinoin are dry skin, irritation and skin peeling. Many of these side effects are most common during the first few weeks of tretinoin treatment. Tretinoin is also linked to an increase in the skin’s sensitivity to sunlight.
Our guide to How to Use Tretinoin Cream goes into more detail about the common and uncommon side effects of tretinoin, and how you can best deal with them.
On the whole, tretinoin’s side effects are mild and rarely result in severe issues for users, even over the long term.
The most common side effects of isotretinoin are dry lips and mouth, crusty or flaky skin, hair and nail issues, nosebleeds and swelling of the lips and/or eyelids. Like tretinoin, isotretinoin can trigger a temporary “purge” period in which acne gets worse before it gets better.
Many of these side effects are temporary, with many isotretinoin users experiencing dry skin, cracked lips and other common side effects in the short term that get better over the course of several months of treatment.
Isotretinoin also has several more severe potential side effects. While rare and not very well-researched, there have been studies linking isotretinoin to things like depression, mood swings, and even suicidal thoughts in some people.
If you have a history of any of the above, be sure to discuss it with your healthcare provider before taking isotretinoin.
Serious — but rare — side effects of isotretinoin also include joint and muscular pain, stomach pain and digestive issues, fever, pain while swallowing and changes to vision. If you experience any of these side effects while using isotretinoin, it’s important to seek immediate medical assistance.
In general, while the most common side effects of tretinoin and isotretinoin are both fairly mild, isotretinoin has a larger and more serious range of potential side effects. However, keep in mind that isotretinoin side effects can be much, much more severe.
Should You Use Tretinoin or Isotretinoin?
So, in the showdown between tretinoin vs. isotretinoin, who should you side with? Tretinoin and isotretinoin are both prescription medications, meaning you’ll need to talk to your healthcare provider about using either one.
Most of the time, tretinoin is used to treat mild to moderate cases of acne. If you have acne that does not respond to non-pharmaceutical creams and washes, daily use of tretinoin is likely to be an effective treatment.
Studies show that tretinoin results in a significant improvement in acne symptoms. In one study, patients given a combination of tretinoin cream and clindamycin one percent gel saw a reduction in acne levels from 13.70 ± 4.80 to 1.30 ± 2.95 after 12 weeks.
This means that tretinoin should be enough to reduce your acne and improve your facial skin to a level with which you’re happy, assuming your acne isn’t extremely severe.
For more severe acne, your healthcare provider might suggest using isotretinoin because of its proven track record.
Ultimately, the best approach is to talk to an experienced, qualified dermatology practitioner about potential solutions for your acne. They’ll be able to let you know which medication is the best solution for your needs, acne and overall health.
Learn More About Tretinoin
Are you interested in using tretinoin as an acne or anti-aging treatment? Our Tretinoin 101 guide covers the essentials of tretinoin, from the medication’s origins and mechanism of action to side effects, scientific studies and more.
You can also learn more about how to use tretinoin to improve your skin and reduce the signs of aging in our guides to using tretinoin for acne and as an anti-aging treatment.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information contained herein is not a substitute for and should never be relied upon for professional medical advice. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment.
Shop this post
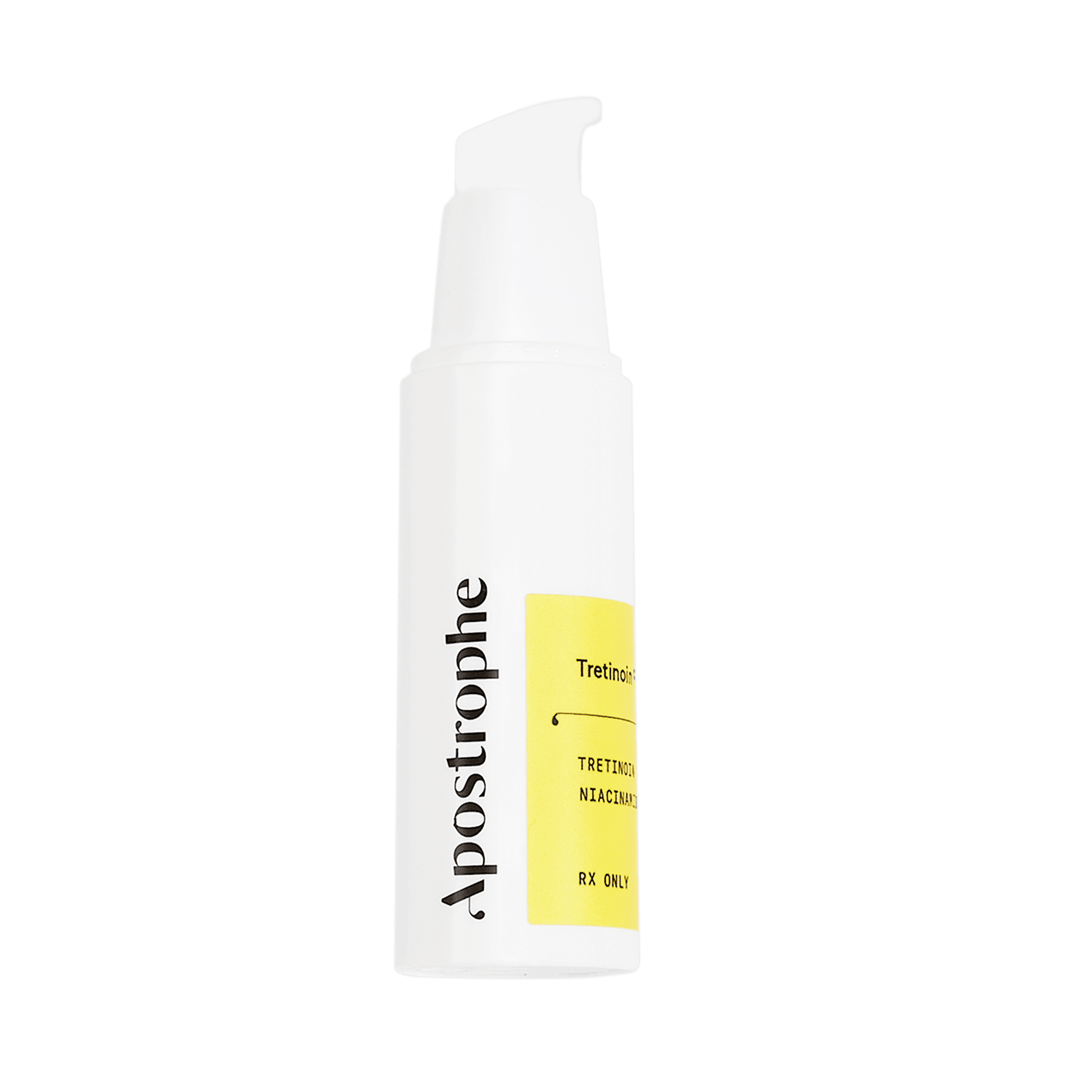

Tretinoin
Like what you just read? Sign up for our email list to get the scoop on skincare science delivered straight to your inbox.

Deep Dives
A dermatologist shares his thoughts on the recent studies about benzoyl peroxide and benzene.
Read More
Education
What is milia?
What is milia? Today, we’re jumping into one type of bump that you may have heard about most commonly in infants — milia.
Read More
Education
Best moisturizer for acne-prone skin
If you have combination acne-prone skin, figuring out which moisturizer is best for your skin might be tough. In this guide, we break down the best moisturizer for combination, acne-prone skin.
Read More
